Kernel Pwn环境搭建
前言
自从上次简单地学了一下kernel之后已经很久没碰了,再捡起来发现还是蛮费劲的,还是写篇博客记录一下环境的搭建,本篇主要参考17、p4nda师兄和x3h1n师姐的博客,中间查了些别的资料,汇总成一篇大杂烩供自己翻阅hh
环境搭建
调试kernel有几种方式,真实漏洞环境大多用Vmware双机调试,或者kvm/qemu,这里介绍CTF里最常用到的qemu方式搭建kernel pwn环境。
编译内核
- 下载指定版本的Linux内核,我是从这里下载的
解压源码目录,内核编译前的配置,这里用图像化配置方式
make menuconfig,有几个选项要勾选(默认应该都会选中)(要先安装sudo apt-get install libncurses5-dev)1
2
3
4
51. kernel hacking->
Kernel debugging
Compile-time checks and compiler options —> Compile the kernel with debug info和Compile the kernel with frame pointers
KGDB
2. save->exit->exitmake -j4(编译前可能要安装库
sudo apt-get install libssl-dev)(编译低版本的内核需要切换低版本的gcc,方法如下)
3.1sudo apt-get install gcc-4.4
3.2sudo update-alternatives --install /usr/bin/gcc gcc /usr/bin/gcc-x x
3.3sudo update-alternatives --config gcc- make modules_install
- make install
之后就可以在./arch/x86_64/boot/bzImage下可以找到bzImage文件,从源码根目录可以拿到vmlinux(bzImage是vmlinuz经过gzip压缩的文件,适用于大内核,vmlinux是静态编译的未压缩的内核,可以在其中找ROP)
编译busybox
启动一个Linux系统除了需要内核外还需要一些必要的命令和文件系统,busybox可以提供这样一个小型的操作系统,可以从官网下载Busybox源码自行编译,这里我选择的是1.30.1,编译前使用make menuconfig将编译选项设置为静态编译1
2make menuconfig
make make install
将生成的_install 文件夹拷贝到linux kernel 源代码根目录
生成文件系统
进入_install目录,创建文件夹)(-p为不存在则创建)1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8mkdir etc
mkdir dev
mkdir mnt
mkdir -p etc/init.d/
mkdir home
mkdir root
touch etc/passwd
touch etc/group
创建./etc/init.d/rcS文件(可以看成系统启动的初始化文件)1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11mkdir -p /proc
mkdir -p /tmp
mkdir -p /sys
mkdir -p /mnt
/bin/mount -a
mkdir -p /dev/pts
mount -t devpts devpts /dev/pts
echo /sbin/mdev > /proc/sys/kernel/hotplug
mdev -s
setsid /bin/cttyhack setuidgid 1000 /bin/sh #normal user
insmod vul.ko
chmod +x rcS
创建./etc/fatab文件(用fstab可以自动挂载各种文件系统格式的硬盘、分区、可移动设备和远程设备等)1
2
3
4proc /proc proc defaults 0 0
tmpfs /tmp tmpfs defaults 0 0
sysfs /sys sysfs defaults 0 0
tmpfs /dev tmpfs defaults 0 0
创建etc/inittab文件(在特定情况下执行的命令,如最后一条是关机的时候卸载所有挂载文件系统)1
2
3
4::sysinit:/etc/init.d/rcS
::respawn:-/bin/sh
::askfirst:-/bin/sh
::ctrlaltdel:/bin/umount -a -r
在dev/创建设备节点(创建两个字符设备)1
2sudo mknod ./dev/console c 5 1
sudo mknod ./dev/null c 1 3
创建文件系统,在_install文件夹中执行find . -print0 | cpio --null -ov --format=newc | gzip -9 > ../initramfs.img
qemu启动Linux kernel
1 | qemu-system-x86_64 -kernel ./linux-4.4.72/arch/x86_64/boot/bzImage --nographic -initrd ./busybox-1.30.1/initramfs.img -m 256M -append "rdinit=./linuxrc -gdb tcp::1234 -S |
gdb远程调试
gdb remote 127.0.0.1:1234即可,注意要先设置arch,set arch i386:x86-64:intel,否则会有g pack too long的报错,
在指定内核中编写驱动程序
linux内核编译前我们用make menuconfig在源码目录生成了一个配置文件.config,这个配置文件表明了内核编译中的一些设置,比如我编译的4.4.72内核默认开启了栈保护,所以七哥栈溢出例子编译之后会有canary和NX,这个是内核决定的,因此要关闭保护只能重新编译内核和驱动(叹气)(后续:重新编译了一次,内核去掉了所有保护,但是驱动仍然有NX,放弃辽)
流程:建个新的文件夹,Makefile:
1 | obj-m := sbof.o |
编译完成之后放到busybox的_install里重新打包,之后就可以调试了
调试
gdb进去之后1
2
3file ./vmlinux
set architecture i386:x86-64:intel
target remote localhost:1234
如果给的文件里只有bzImage可以自己提取,脚本地址
在qemu中查看加载的程序基址1
cat /sys/modules/sbof/sections/.text
在gdb中添加符号文件1
add-symbol-file ./sbof.ko 0xffffffc0000000
查看commit_creds和prepare_kernel_cred函数的地址1
2cat /proc/kallsyms | grep commit_creds
cat /proc/kallsyms | grep prepare_kernel_cred
小知识
/proc文件系统是一个虚拟文件系统,可以在/proc中动态创建虚拟文件,通过对虚拟文件的读写与实现与内核的通信。可以使用以下函数创建虚拟文件
1 | //第三个参数是文件在/proc中的位置,默认为/proc |
kptr_restrict控制/proc/kallsyms是否显示symbols的地址,通常会在init文件中给出限制:1
echo 1 > /proc/sys/kernel/kptr_restrict
dmesg_restrict限制非特权用户读取dmesg信息,无法访问内核打印的消息,通常会在init文件中给出限制:
1 | echo 1 > /proc/sys/kernel/dmesg_restrict |
kernel pwn保护机制
KASLR
内核地址随机化,相当于ASLR(并非默认启用,需要在内核命令行中加入kaslr开启)
SMAP/SMEP
SMAP(Supervisor Mode Access Prevention,管理模式访问保护):
禁止内核访问用户空间的数据
SMEP类似于NX,即内核态无法执行shellcode,linux内核从3.0开始支持SMEP,3.7开始支持SMAP。
Stack Protector
在编译内核时设置CONFIG_CC_STACKPROTECTOR选项,即可开启该保护,一般而言开了这个保护再编译驱动会发现有canary。
Kernel UAF
CISCN-babydriver
驱动逻辑
因为是第一次分析,所以写的详细一点,从_init函数开始,首先用alloc_chrdev_region函数动态分配一个设备号,成功分配的话初始化一个cdev结构体(每个字符设备对应一个结构体),_class_create注册一个字符设备,创建相应的class,再调用device_create创建对应的设备,注意每个地方失败都会有回滚操作(destroy或者unregister)
1 | int __cdecl babydriver_init() |
_exit是设备卸载时候的会调用的,把分配的设备和class等回收。
1 | void __cdecl babydriver_exit() |
open函数的参数有inode和filp,每一个设备都会对应一个inode,而且是共享一个inode,这个不像filp文件指针每次打开一个设备都会创建一个新的文件指针以供操作(内核里的文件指针,跟用户态不一样)
1 | int __fastcall babyopen(inode *inode, file *filp) |
read函数是从内核往用户态读数据,kernel里的文件结构体定义了一组基础接口,允许开发者按照参数的标准实现一套自己的函数,read write open release(close)都是自己实现的,这里的read判断babydev_struct.device_buf不为NULL就将用户输入的第三个参数length长的数据从device_buf拷贝到Buffer里
1 | ssize_t __fastcall babyread(file *filp, char *buffer, size_t length, loff_t *offset) |
write是从用户态拷贝length长的数据到babydev_struct.device_buf里,这里的IDA反汇编优点问题,看asm可以看到copy_from_user的参数
1 | ssize_t __fastcall babywrite(file *filp, const char *buffer, size_t length, loff_t *offset) |
ioctl是最简单的和设备通信的方式,开发者可以在其中根据arg参数决定对设备不同的操作,这里注意command需要是一个唯一的数字,否则可能会进行其他未知的操作,在新的标准里command是有结构的,不同的位有不同功能,这里也不深究了,如果command是0x10001,则释放device_buf,再分配一个指定size的内存地址赋给device_buf。
1 | // local variable allocation has failed, the output may be wrong! |
release函数调用发生在关闭设备文件的时候,这里会free掉buf
1 | int __fastcall babyrelease(inode *inode, file *filp) |
漏洞利用
这里的漏洞出现在驱动没有处理好并发,在驱动开发的时候,驱动必须是可重入的,也就是说必须是可以支持被多次打开的,这里release的kfree之后没有清空全局变量babydev_struct.device_buf,全局变量在两次打开设备文件的时候是共享的,也就是说如果我们两次打开设备,在第一次free掉buf,在第二次仍能继续读写数据。
最简单的利用方式是阅读该版本的linux源码,获取struct cred的大小(这里是0xa8),在第一个设备操作中关闭文件free掉buf,再fork一个新的进程,每次fork的时候会分配一个struct cred结构体来标明进程的权限,这个结构体会将父进程的cred复制过来,分配到的恰好是我们分配的结构体(slab分配器类似fastbin的分配方式),这时候我们在父进程里通过write修改全局变量的device_buf,实际上是修改cred,我们把uid改为0即可在子进程提权,之后在其中打开shell即可
1 | struct cred { |
编写exp
exp拿c写,cred的前28个字节改为0即可,exp如下:
1 |
|
TSCTF2019->babykernel
程序分析
比赛的时候没做出来,半年之后过来考古233.
ioctl有几个功能:
- cmd=
0x22B8,往BUY_LIST[arg3]赋值0x123456789ABCDEF0LL - cmd=
0x271A,固定分配0xd0的obj到BUY_LIST[arg3]并执行*(_QWORD *)(BUY_LIST[arg33] + 8) = 0LL;等赋值命令 - cmd=
0x2766,释放BUY_LIST[arg3],这里有double free - cmd=
0x1A0A,同1一样赋值BUY_LIST[arg3]为0xFEDCBA987654321LL
漏洞到这里已经很清楚了,bss上的全局变量释放后未清空,保护有smap和smep,调试可以看到(源码也可以直接看)cred大小恰为0xd0,所以我们释放一个obj,随后fork进程复用这个obj,在主进程再次释放此obj随即alloc到它,之前的*(obj+8)可以将uid位清零,子进程的权限提升为root。
1 | signed __int64 __fastcall tshop_ioctl(__int64 arg1, unsigned int arg2, unsigned int arg3) |
exp.c
1 |
|
Kernel ROP
QWB2018-Core
寻找rops
vmlinux是未经压缩的二进制文件,可以使用ropper --file ./vmlinux > rops将寻找的rop存放起来,如果题目没有给vmlinux可以拿extract-vmlinux进行提取./extract-vmlinux ./bzImage > ./vmlinux
漏洞分析
查看启动脚本,发现开了kaslr保护,解压cpio文件cpio -idm < ./core.cpio,文件夹下有系统的初始化脚本init,其内容为。
1 |
|
前面实在创建设备驱动,挂载设备,之后将kallsyms的内容拷贝到/tmp/kallsyms文件中,kptr_restrict为1表示root用户可以读取内核符号地址而普通用户不能。同理dmesg_restrict为1表示root用户可以查看dmesg信息而普通用户不能。
后面是设置网卡和路由信息,启动了一个uid为1000的普通用户所在的shell,poweroff这行是设置120s定时关机,我们为了避免干扰做题先注释掉,同样为了之后能看text段的基址我们把uid改成0,即root用户。
最后的insmod插入了一个内核模块core.ko,这个就是本题的漏洞模块,我们等会来分析它。现在把文件系统重新打包(文件系统中有个打包脚本,参数为打包的压缩文件名,打包之后拷到上层目录即可)
下面分析core.ko
在ioctl函数里实现了几种功能,其中arg1表示choice,arg2为参数2。
- arg1=0x6677889B时,调用core_read(arg2),从v4[off]拷贝0x40长度的数据到arg2指定的用户地址,这里off是一个全局变量
- arg1=0x6677889C,将arg2赋值给off(结合1和2我们可以泄露栈上数据)
- arg1=0x6677889A,调用core_copy_func,arg2指定size,拷贝arg2长度的数据从name到栈局部变量v1,这里检查了size要小于等于0x3f,但是qememcpy用的类型是int16,因此我们传入一个负数即可绕过检查(因为size指定,这里可以栈溢出)
- core_write函数把用户空间的数据拷贝到bss的全局变量name上,size也是用户指定的长度
1 | __int64 __fastcall core_ioctl(__int64 a1, int arg1, __int64 arg2) |
漏洞利用
我们现在有地址泄露和栈溢出,用到的就是这里讲到的kernel rop,思路如下:
- 利用ioctl结合core_read泄露地址及canary
- 利用core_write吧gadgets写到name上
- 利用copy_func将gadgets写到栈上
- 通过rop执行
commit_creds(prepare_kernel_cred(0)) - 返回用户态,执行system(“/bin/sh”)起shell(使用
swapgs;iretq来进行切换,但最开始要使用save_status保存寄存器的状态)
1 | size_t user_cs,user_ss,user_rflags,user_sp; |
调试
tips1:ctrl+A再按X可以让qemu退出
使用gdb ./vmlinux -q调试内核,在qemu内部使用cat /sys/module/core/sections/.text查看基址,使用add-symbol-file ./core.ko [text_base]增加符号表,b core_read添加断点,target remote localhost:1234开始调试。
exp.c
最后在构造rop的时候的栈结构是
p_rdi
0
prepare_kernel_cred
mov rdi, rax
commit_creds
但是gadgets里没有直接能用的mov rdi, rax; ret;所以这里迂回了一下。构造的结构是:
p_rdi
0
prepare_kernel_cred
p_rdx_ret
p_rcx_ret
mov rdi, rax; call rdx;
commit_creds
注意写exp之前要先sava_status,在 64 位系统中执行 iretq 指令前需要执行一下 swapgs 指令,该指令将 gs 寄存器的值与 MSR 地址 中的值交换。在内核态常规操作(如系统调用)的入口处,执行 swapgs 指令获得指向内核数据结构的指针,那么对应的, 从内核态退出,返回到用户态时也需执行一下 swapgs
iretq用来恢复用户空间,需要给出之前保存的寄存器的值。恢复到用户空间之后一个ret到我们的system("/bin/sh")即可起root shell。
还有一个有意思的地方在于我们明明是在write里泄露的canary,在copy函数里进行的栈溢出,但是canary和栈布局都是一样的,而且在gdb中看到的输入地址距离rbp相去甚远,实际上却恰如其分。
1 |
|
ret2usr
简介
利用的是内核态位于ring 0,可以执行用户态的函数,我们不必自己构造调用链,而可以直接在用户态构造好我们需要的函数,在内核rop的时候直接调用即可,当然这些函数用户态是没有的,我们还是得先泄露出来。exp编写如下:
1 |
|
bypass smep
简介
smep保护其实就是为了防止ret2usr这样的攻击,是否开启这个保护取决于rc4寄存器的值,我们一般只需要给它改成一个固定值0x6f0就可以关闭它,这里用之前Kernel UAF的babydriver进行演示
CISCN2017-BabyDriver
漏洞利用
这里我们选择一个tty_struct结构体进行操作,在open("/dev/ptmx",O_RDWR);的时候会分配这样一个结构体,其源码如下:
其中tty_operations结构体有许多函数指针,我们可以通过伪造fake operation来劫持控制流。
1 | struct tty_struct { |
思路是利用UAF泄露出部分tty_struct结构体的内容,我们把operation这个结构体指针改成我们伪造的函数结构体指针,在函数结构体指针中按照顺序改三个指针为gadgets和rop,最终在调用write的时候触发这些函数执行劫持控制流,rop之后先改rc4,后面都一样。
1 |
|
Double Fetch
简介
Double Fetch是一种类似条件竞争的攻击方式,原理是内核在调用用户空间数据的时候可能会先做安全检查,随后调用其数据指针,而第二次取数据处理的时候可能使用被篡改的恶意数据。
2018 0CTF Finals Baby Kernel
漏洞分析
flag是编码到bss上的,我们要做的是通过一些校验,即可得到输出的flag。
ioctl主要有两个功能,cmd=0x6666的时候输出flag的地址到dmesg里,cmd=0x1337的时候开始进行校验。检查的内容是指针是否是用户态空间数据,指针内部的flag_str指针是否是用户态数据,非用户态的话会直接返回,第三个检查是flag_str的长度是否和flag长度一致,我们这里利用double fetch的漏洞,先从dmesg里得到flag的地址,之后构造恶意线程不断往用户态的一个数据指针里修改flag_str为内核flag地址,这样在经过三次校验之后有一定几率在校验flag字节前把flag_str改为实际flag地址,之后即可输出flag。
1 | signed __int64 __fastcall baby_ioctl(__int64 a1, __int64 arg1) |
exp.c
1 |
|
Heap Overflow
简介
之前介绍的大部分都是栈的内容,内核堆漏洞也是蛮多的,最简单的莫过于堆溢出,因为slab的分配类似fastbin,我们可以通过溢出覆盖下一个free_chunk的fd两次分配到任意地址。
SUCTF 2019 sudrv
漏洞利用
ioctl给了仨功能,分别是分配、释放和输出堆块内容,其中sudrv_ioctl_cold_2函数有格式化字符串漏洞,可以通过%llx泄露栈上的内容,进而从dmesg里获取泄露的函数相关地址以及栈地址,通过堆溢出(write未检查buf和size)我们可以分配到堆到栈上进行溢出写rop。
除此之外,我们还可以通过劫持modprobe_path不起root shell但是可以以root身份执行任意命令,比如把flag拷贝到/tmp目录下并给777权限之后查看。这个原理是内核在运行异常的时候会调用modprobe_path指向的文件,我们改成自己编写的getflag.sh即可,执行完exp之后手动取执行/tmp/ll(一个格式错误的可执行文件)即可触发读取flag。
1 | __int64 __fastcall sudrv_ioctl(__int64 a1, int cmd, __int64 arg2) |
注意在这里的modprobe_path在/proc/kallsyms里没有符号,我们可以通过引用找到它参考,先找到__request_module函数,在gdb里查看函数汇编即可找到modprobe_path。在这里未开kalsr的时候是0xffffffff822423201
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38/ # cat /proc/kallsyms | grep __request
ffffffff81065210 t __request_resource
ffffffff81065d60 T __request_region
ffffffff810833e0 T __request_module
ffffffff8108378b t __request_module.cold.4
ffffffff810b2c10 T __request_percpu_irq
gdb-peda$ x/28i 0xffffffff810833e0
0xffffffff810833e0: push rbp
0xffffffff810833e1: mov rbp,rsp
0xffffffff810833e4: push r15
0xffffffff810833e6: push r14
0xffffffff810833e8: push r13
0xffffffff810833ea: mov r13,rsi
0xffffffff810833ed: push r12
0xffffffff810833ef: movzx r12d,dil
0xffffffff810833f3: push r10
0xffffffff810833f5: lea r10,[rbp+0x10]
0xffffffff810833f9: push rbx
0xffffffff810833fa: mov ebx,edi
0xffffffff810833fc: sub rsp,0xb8
0xffffffff81083403: mov QWORD PTR [rbp-0x50],rdx
0xffffffff81083407: mov QWORD PTR [rbp-0x48],rcx
0xffffffff8108340b: mov QWORD PTR [rbp-0x40],r8
0xffffffff8108340f: mov QWORD PTR [rbp-0x38],r9
0xffffffff81083413: mov rax,QWORD PTR gs:0x28
0xffffffff8108341c: mov QWORD PTR [rbp-0x68],rax
0xffffffff81083420: xor eax,eax
0xffffffff81083422: test dil,dil
0xffffffff81083425: jne 0xffffffff810835a6
0xffffffff8108342b: xor r15d,r15d
0xffffffff8108342e: cmp BYTE PTR [rip+0x11beeeb],0x0 # 0xffffffff82242320
0xffffffff81083435: jne 0xffffffff8108345e
0xffffffff81083437: mov rcx,QWORD PTR [rbp-0x68]
0xffffffff8108343b: xor rcx,QWORD PTR gs:0x28
0xffffffff81083444: mov eax,r15d
gdb-peda$ x/s 0xffffffff82242320
0xffffffff82242320: "/tmp/getflag.sh"
exp.c
exp来自17学长,在测试这个fastbin分配机制的时候我试了下改size,0x700、0x600和0x900均不行,最后是0x800和0x400成功,挠头.jpg,找了下也没有讲的很好的slab/slub分配机制的文章,回头再说好了。
使用的时候使用管道作为输入printf '\x20\x23\x24\x82\xff\xff\xff\xff' | ./exp,执行完exp之后执行/tmp/ll再cat /tmp/flag即可。
1 |
|
prctl爆破cred地址
简介
是p4nda师傅介绍的三种权限提升思路,第一种也是最简单的思路就是直接修改cred结构体对应标识权限的数据为0,这里用到了一个leak cred地址的方式,首先我们要知道一些基础知识。每个线程在内核中都对应一个线程栈,一个thread_info结构体,这个结构体如下:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9struct thread_info {
struct task_struct *task; /* main task structure */
__u32 flags; /* low level flags */
__u32 status; /* thread synchronous flags */
__u32 cpu; /* current CPU */
mm_segment_t addr_limit;
unsigned int sig_on_uaccess_error:1;
unsigned int uaccess_err:1; /* uaccess failed */
};
在这个结构体中cred结构体用以标识线程的权限,在cred结构体后8字节的位置有一个字符数组char comm[TASK_COMM_LEN];用来表示进程名(不超过16字节),我们可以用prctl设置它的内容之后用任意读穷举搜索其位置,进而定位到cred地址,之后结合任意写改其内容即可。
1 | struct task_struct { |
xman结营赛 OOB
程序分析
这个题坑还挺多的(还是我太菜了),启动脚本去掉定时关机,去掉aslr方便调试。
1 |
|
新建一个文件夹把cpio拷进去,执行cpio -dmv < rootfs.cpio解压出文件系统,到./etc/init.d里去改rcS(这里的init脚本为空),初始脚本里没有挂载/sys目录导致我们没法看更多信息(lsmod可以查看模块.text的加载基址),可以先拿root起,方便看函数地址等。
1 |
|
另外进去之后看一眼/dev/OOB的权限会发现普通用户是只读的,我平时open的时候参数习惯为2表示可读写,现在普通用户只能为0,否则文件打开会失败。
OOB.ko里其实只有一个ioctl,里面有四个命令,分别对应Malloc、Free、Write和Read,仔细观察一下我们可以控制idx、user_buf、stack_size和stack_idx而在R/W的时候没有对idx进行检查,虽然他是一个unsigned int的类型,但是我们可以往前任意读,我们Malloc的对象是一个0x100大小的对象,其地址作为obj的addr和0x100存储在bss上,如果bss_list高地址有一些数据满足条件我们就可以任意读了(stack_idx + stack_size <= obj_idx1->size)这里的stack_idx可以看成addr的offset(单字节),stack_size为我们想读取的数据大小,其相加小于size,因为我们不能事先在bss上写东西,因此只能往前找满足条件的fake_obj。
1 |
|
一番努力之后终于找到了满足条件的地方,bss_list地址为0xffffffffa0002420,用这个obj我们可以读取[0x000d00620000002e,0x000d00620000002e+0xffffffffa0002420)范围内的地址的值
1 | 0xffffffffa0003090: 0x000d00620000002e 0xffffffffa0002420 |
显然bss_list是满足这个条件的
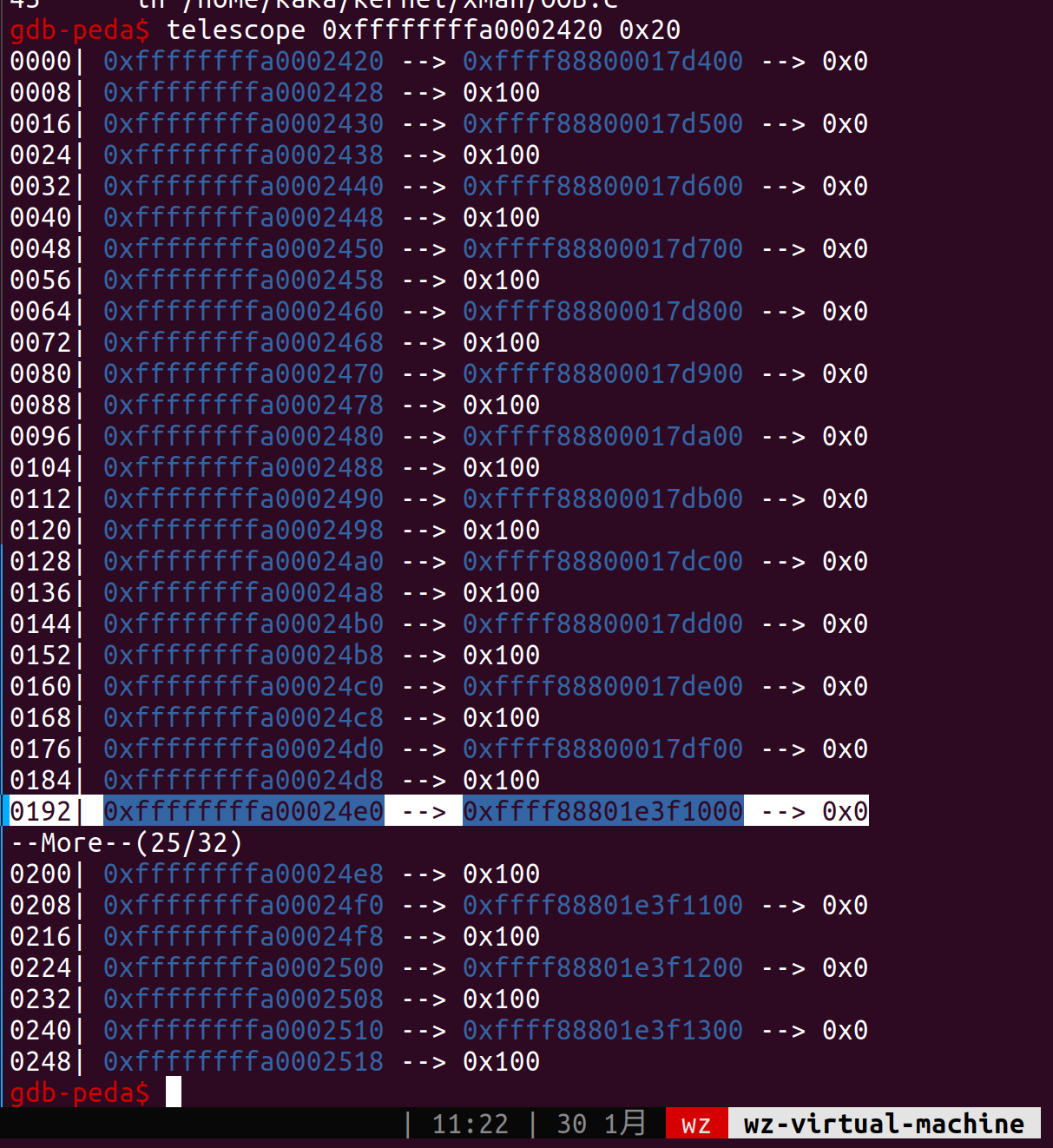
尝试多次分配,发现分配12次之后之前的slub缓存就用完了,会用Buddy分配新的一块区域供继续分配,至此我们的思路就有了,分配完这些内存然后fork一个进程,触发创建新的cred对象,这个对象地址一定在0x*17df00和0x*1e3f100之间,我们就可以爆破这块内存区域,寻找我们prctl设置的进程名,进而搜到cred。
下一步用任意地址读读取cred里前0x100的内容,修改前0x28字节为usr_buf。再用任意地址写写到free后的slab的fd,两次Malloc可以得到cred对象,把usr_buf拷贝进去后即可提权成功。
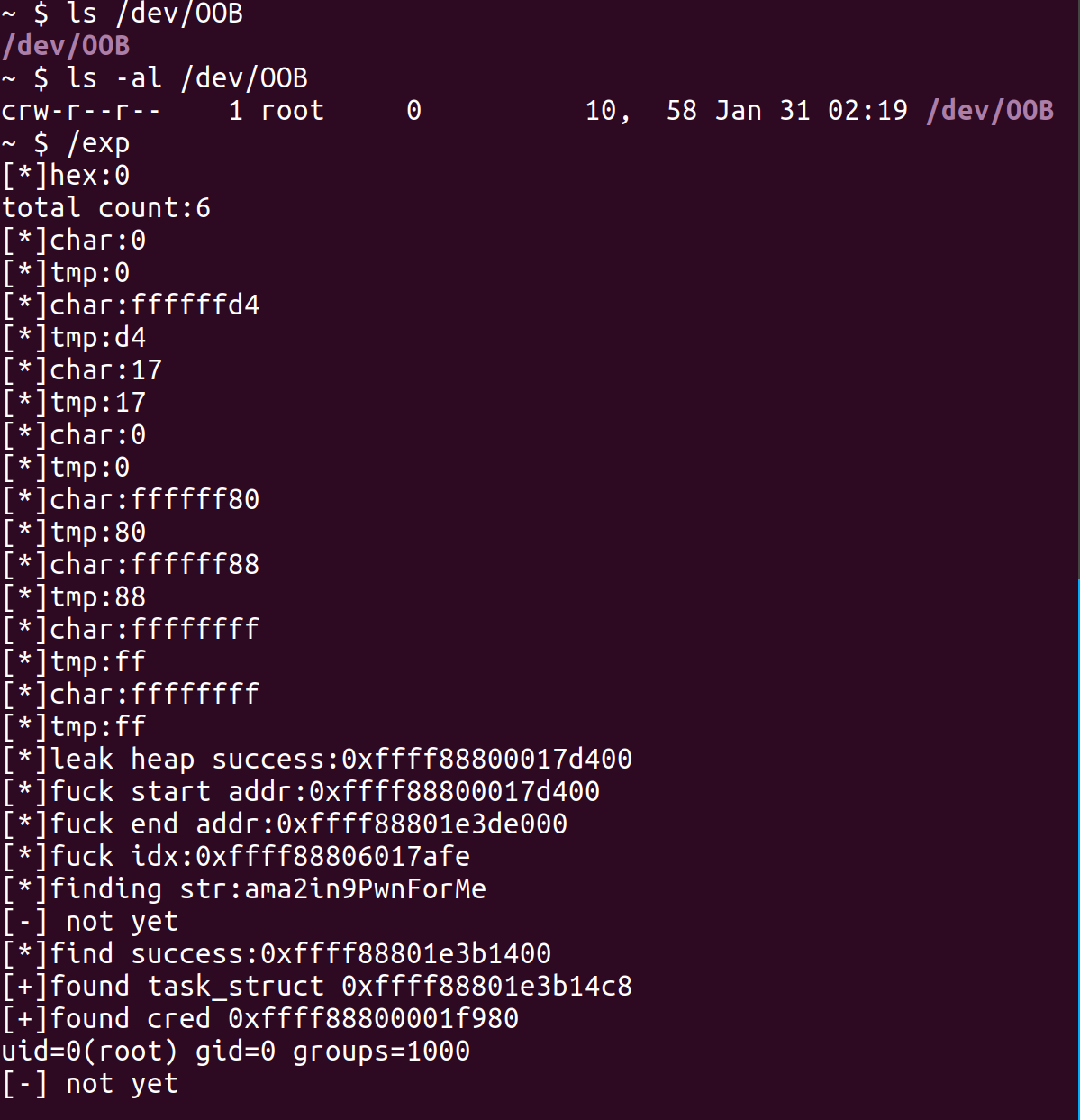
exp.c
这里还有地方是我没想明白的,就是我以为自己修改的cred是子进程里的,没想到就是本进程的,之前一直在子进程起shell,卡了很久
1 |
|
使用userfaultfd缺页扩大窗口期
介绍
之前想复现n1ctf的babykernel和de1ctf的race,发现官方题解中都有mmap的部分,一直不是很理解,终于在先知上找到一篇相关的文章,写的非常详细,因此自己实践了一下(照着exp打了一遍),记录一下userfaultfd的使用
BalsnCTF2019 KrazyNote
背景知识
页和虚内存
内核的内存主要有两个区域,RAM和交换区,将要被使用的内存放在RAM,暂时用不到的内存放在交换区,内核控制交换进出的过程。RAM中的地址是物理地址,内核使用虚拟地址,其通过多级页表建立虚拟地址到物理地址的映射
页调度和延迟加载
有的内存既不在RAM又不在交换区,比如mmap出来的内存,这块内存在读写它之前实际上并没有被创建(没有映射到实际的物理页),例如mmap(0x1337000, 0x1000, PROT_READ|PROT_WRITE, MAP_FIXED|MAP_PRIVATE, fd, 0);实际上并没有把fd对应的内容拷贝到这块区域,只是将地址0x1337000映射到fd这个文件。
当有以下代码访问时:
1 | char *a = (char *)0x1337000 |
内核会做以下事情:
- 为0x1337000创建物理帧
- 从fd读取内容到0x1337000
- 增加一个页表的索引
总之,如果是初次访问mmap的页,耗时会很长,导致上下文切换以及当前线程的睡眠
别名页
没有ABI可以直接访问物理帧,但内核有时候需要需要修改物理帧的值(例如修改页表入口),于是引入了别名页,将物理帧映射到虚拟页。在每个线程的启动和退出过程中,一般都有两个物理帧映射到它。别名页的地址一般是SOME_OFFSET+physical_addr
userfaultfd机制
这个机制可以让用户自己处理缺页,可以在用户空间定义一个userfault handler,用法见官方文档。大概步骤如下:
- 创建一个描述符uffd:所有的注册区间、配置和最终缺页处理都需要ioctl对这个fd进行处理。我们可以用UFFDIO_REGISTER注册一块监视区域,这个区域发生缺页的时候使用UFFDIO_COPY向缺页地址拷贝数据
- 用UFFDIO_REGISTER注册监视区域
- 创建专用线程用来轮询和处理缺页事件
观察可以发现其中大部分操作都是固定的,我们可以自己整理一个头文件加进去,用的时候很方便。
1 |
|
漏洞分析
这个内核模块逆的时候看起来很麻烦,结合别人博客的分析搞清楚了逻辑,其实是在bss上一块大小为0x2000的区域模拟heap的分配,首先搞清楚我们输入的数据结构和内核模块存储的单个数据结构。用户输入的结构体类型为UserAttr,其中idx指明note的索引,length对应分配的大小,user_buf为拷贝到note里content_arr的字符串或者从中读取数据的字符串。
一个note struct由四个成员组成,第一个是key,这个值根据原作者的分析是task_struct.mm->pgd,页全局目录的存放位置),length是后面content_arr动态数组的大小(最大不超过0x100),contentPtr保存的是content_arr-page_offset_base这里的page_off_base就是我们之前提到的那个别名页的SOME_OFFSET。最后的content_arr是一个动态数组,其大小由New的时候用户给的length决定
1 | /* |
从init_module开始,注册了一个设备在0x620,设备名下面就是用户自己定义的file_ops,而0x680全是空,也就是说全部使用默认的操作函数。看下源码会发现这里的ioctl是unlocked_ioctl也就是存在竞争
1 | __int64 __fastcall init_module(__int64 a1, __int64 a2, __int64 a3) |
继续分析模块的功能会发现实现了四个功能,分别是New、Delete、Show和Edit。其中New的功能就是根据用户给的length从全局的内存中取一块作为notes[req.idx]并分配一块content_arr[length],之后将全局指针对应向后偏移,拷贝的用户数据要先异或key再存入其中
1 | if ( (unsigned int)arg2 <= -'\xFF' ) |
Delete函数清空全局内存区并将分配的指针指向开头。
1 | if ( (_DWORD)arg2 != -254 ) |
Show函数按照notes[idx].length把content_arr内容拷贝到用户态空间,这个过程是先拿contentPtr+page_offset_base找到content_arr,再把其中的内容异或key拷贝
1 | v10 = notes[idx]; // -254->show |
Edit函数和Show差不多,也是先计算再拷贝,这里的问题就是copy_from_user并不是原子性的操作,也并没有上锁,按照我们之前的分析缺页可以让其有一个很大的空窗期供我们操作,进而利用竞争改掉某些关键数据
1 | if ( (_DWORD)arg2 == -'\xFF' ) // -255->edit |
漏洞利用
我们先创建一个buf为0x10大小的note0,在Edit的过程中我们利用usefaultfd的handler在成功拷贝之前释放所有note,再创建一个新的Note0和Note1,其buf大小均为0,在使用ioctl向缺页部分拷贝的时候我们把这个页的buf[8]改为0xf0,这样拷贝之后原来buf[8]的部分实际上是note1.length,进而我们可以越界读写note1。
- leak key:直接
Show(1),因为我们把note1的length改为了非零值,因此会输出0 xor key,得到Key值 - leak module base:注意我们现在泄露的只是一个相对值(module_base-page_offset_base),但是无所谓,因为最终show的时候会加上这个偏移。创建Note2则
note2.contentPtr即为note2.content_arr-page_offset_base,show(1)即可泄露出来这个值,再减去它到模块基地址的偏移即为模块相对基址 - leak page_offset_base:泄露这个值就比较麻烦了,我们先来看一个指令
000000001F7 4C 8B 25 12 2A 00 00 mov r12, cs:page_offset_base,这个调用实际含义是mov r12,[rip+offset],而这个offset存储在module_base+0x1fa,我们的思路就有了,先修改note2的key为0,length为4,contentPtr为module_base+0x1fa,得到这个4字节的偏移,再用相同方式泄露出(module_base+0x1fe)+offset的值,即为所求 - leak cred:通过之前提到的search搜索的方式
- 用任意写修改cred的对应数据位
- execv(注意不是execve)起新的shell(这个shell会继承当前进程的uid)
exp.c
如前所述基本是照着打了一遍,再次感谢bsauce师傅的文章
1 |
|
ret2dir
简介
这种攻击最早是在DE1CTF见到的,当时ycx学长的博客有相关实践,当时对于内核完全摸不着头脑,现在大概懂了一些基本trick,翻一下de1ta在先知给的writeup,尝试学习一波。
DE1CTF Race
程序分析 && 漏洞利用
跟之前那道题差不多,先看下自己实现的fops,发现全是空,ioctl是没有上锁的,copy_from_user和copy_to_user都是非原子操作。实现了New、Edit、Show和Delete功能。之前那道题目提到了别名页,实际上就是这里的physmap。
开始我自己想用的是之前提到的userfaultfd来保证竞争的结果可控,后来发现这个API好像用不了,只能利用mmap缺页造成的短暂中断间隙进行竞争删除。
官方的给的思路前面是用到了physmap的特性,就是这个地址的基址实际上是物理地址physical_addr+offset,可以绕过地址随机化。我们在Show的时候竞争删除,从而泄露出slab地址,根据官方的解释physmap的地址应该在slab前面,且包含slab,这个个人感觉是有依据的,之前在做xman那道题的时候看p4nda师傅博客给的爆破地址的起始地址就是没有开地址随机化的physmap位置。
猜测了physmap地址(不一定是起始地址,但是是在这个区域中的一个地址),我们先用堆喷占位physmap区域,为了提高命中率我们分配的内存大小为64M,是整个进程的一半。在Edit的时候竞争删除,从而可以往slab的fd竞争写入刚才猜的地址。
后面官方的做法是分配tty_struct结构体,因为我们现在slab从physmap开始分配,tty_struct会分配到这块区域,之后我们check堆喷到的内存查看有无非零区域(tty_struct结构体里有一堆函数指针),遇到非零值就说明找到了slab_addr并可以通过函数指针及偏移找到vmlinux_base,再往后官方是从tty_struct下手,我觉得既然有竞争的UAF可以改modprobe_path,应该更简单一点。
exp.c
自己实在是懒得写(或抄)exp,作为kernel入门篇的最后一篇文章也还是以官方的writeup收尾。注意这个exp后面有一个自己写内核shellcode的部分需要自己补充(这就是为什么我说不如改modprobe_path方便的原因)
1 |
|
思考
这种攻击非常非常类似于去年TSCTF鸡哥出的题,同样都是堆喷,同样都是改一个值之后爆破打印确定其位置,再次膜w1tcher和p4nda师傅。
总结
这篇文章断断续续写了两个月大概,写kernel的exp太累,尤其是多线程/进程不好调试的题目,收获到了很多东西,todolist本来还有n1ctf的一道题,但是看了题解觉得自己的功力还不够,下一步的目标是复现两个想了很久的内核CVE。不知不觉已经正月十五了,寒假又废了,希望这俩CVE对我好一点qwq。

