CVE-2019-6788 Qemu逃逸漏洞复现与分析
前言
CVE-2019-6788是一个QEMU的堆溢出漏洞,本篇文章基于raycp师傅的分析复现,中间补充一些细节方便自己理解。
环境搭建
手里有GEEKPWN2020决赛的一道qemu的题目,那道题是改的这个CVE,因此我直接拿过来用了,不过对比了一下它和raycp师傅的脚本,发现没什么区别,估计也是出题人直接拿来用的。
下面是创建文件系统的脚本,需要提前装debootstrap,我没挂代理然后挂了一宿才下完2333.当前目录下的ssh/id_rsa为ssh的私钥。
1 | mkdir qemu |
启动脚本如下:其中hostfwd做了端口转发,因此我们传输文件可以使用scp -i ./ssh/id_rsa -P2222 ./1 root@localhost:/。内核文件随便找一个就可以。
1 |
|
在github下载qemu的源码,切换到漏洞版本,编译即可。这里直接搬运raycp师傅的命令。如果觉得慢,可以拿hub.fastgit.org替换github.com然后走https clone。下面的configure开启了调试,因而最后的bin文件包含符号表。
1 | git clone git://git.qemu-project.org/qemu.git |
本漏洞复现于ubuntu 18.04,gcc的版本如下。
1 | wz@wz-virtual-machine:~/Desktop/CTF/CVE-2019-6788/start_qemu$ gcc -v |
启动之后宿主机的ip为10.0.2.2,虚拟机ip为10.0.2.15,由于是持久化的磁盘文件,因此可以使用apt install net-tools安装net-tools来使用ifconfig命令。
漏洞分析
为了确定编译和环境没有问题,我们先打一发poc,poc代码如下,从虚拟机中连接宿主机的113端口,需要先在宿主机中用sudo nc -lvknp 113监听113端口,这里-k参数可以保证端口持续监听,这样就不用每次手动重新启动nc。
1 |
|
编译之后scp传到虚拟机中,执行后qemu崩溃,poc攻击成功。
根据wp将断点断到tcp_emu函数,一直continue直到崩溃产生,打印一下调用栈,
1 | gdb-peda$ bt |
查看位于slirp/tcp_subr.c的函数实现,so_rcv的类型为struct sbuf *,它存储的是tcp协议的数据,m的类型为struct mbuf *,它存储的是ip协议的数据,这里的memcpy(so_rcv->sb_wptr, m->m_data, m->m_len);将网络层的数据保存到了传输层中。这两个数据结构的定义如下。
1 | struct sbuf { |
当传输的数据中包含有\r|\n时,会对so_rcv->sb_cc赋值,否则保持其默认值0,我们发送的payload中不包含有\r\n,因此sb_cc不会被赋值。
1 | int |
我们继续往下看其调用函数tcp_input,位于slirp/tcp_input.c中。ti为struct tcpiphdr类型的变量,其定义如下。ti_len表示协议长度,由于拷贝之后sb_cc还是为0,因此会使用sbappend(so, m)->sbappendsb进行追加拷贝,从而造成堆溢出。
1 |
|
我们动态调试一下,验证自己的猜想,断点断到比较和memcpy处.
1 | directory /home/wz/qemu/slirp/tcp_input.c |
可以看到ti_len一直为我们输入的长度0x500,sb_datalen为0x2238的固定值,因为sb_cc为0,因此这里的比较恒成立,故而持续拷贝造成堆溢出。
1 | gdb-peda$ p *ti |
断点第二次断到了拷贝函数,拷贝之后我们可以看到sb_wptr已经存放了输入数据,而sb_cc仍为0,而比较函数仍可以通过。
1 | gdb-peda$ p *so_rcv |
再过一次拷贝,sb_wptr继续递增,直到超出分配的0x2238的空间,最终覆盖某些关键数据结构造成crash。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30gdb-peda$ p* so_rcv
$14 = {
sb_cc = 0x0,
sb_datalen = 0x2238,
sb_wptr = 0x7f3f78205900 "\264",
sb_rptr = 0x7f3f78205900 "\264",
sb_data = 0x7f3f78204f00 'A' <repeats 200 times>...
}
gdb-peda$ p* m
$15 = {
m_next = 0x7f3f78213600,
m_prev = 0x55ea40fc04a8,
m_nextpkt = 0x0,
m_prevpkt = 0x0,
m_flags = 0x4,
m_size = 0x608,
m_so = 0x7f3f7850c000,
m_data = 0x7f3f78208b24 'A' <repeats 200 times>...,
m_len = 0x500,
slirp = 0x55ea40fc0400,
resolution_requested = 0x0,
expiration_date = 0xffffffffffffffff,
m_ext = 0x0,
m_dat = 0x7f3f78208ad0 ""
}
gdb-peda$ x/8gx 0x7f3f78204f00-0x10
0x7f3f78204ef0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000002245
0x7f3f78204f00: 0x4141414141414141 0x4141414141414141
0x7f3f78204f10: 0x4141414141414141 0x4141414141414141
0x7f3f78204f20: 0x4141414141414141 0x414141414141414
漏洞利用
这里的exp是分析的raycp师傅的,因为编译环境和运行环境不太一样,中间调整了一些变量的值。
malloc原语
qemu的堆排布非常复杂,我们想要控制堆,就需要先将空闲的堆块分配完,之后从top_chunk开始分配,方可通过可控的堆溢出覆写某些数据结构。首先让我们重温一下IP协议。
如下图所示是一个IP数据包的示意图,linux下的数据结构对应图里的各个字段。
重点关注Flags字段和Fragment Offset字段。
- Zero:Unused,置为0
- Do not fragment flag:表示数据包是否为分片数据包,当置为1时,表示未分片,简写为DF位
- More fragments following flag:表示后续还有没无分包,有的话置为1,简写为MF位
- Fragment Offset:当前数据包在整个大数据包中的偏移offset。
IP包的total_length用2字节表示,因此一个IP数据包最大为65535字节,一旦要发送大量数据时我们需要对数据包进行分段传输,我们看下qemu对于这部分功能的实现。
1 | /* |
该函数位于slirp/ip_input.c中,每次遇到一个分片的数据包时(IP_DF=0),分配一个mbuf指针类型的链表用以存放分包,这里的g_malloc经过调试分配的大小为0x668。
因此我们构造DF=0的IP协议包,多次发送清空空闲内存。(这里的链表指针只有当接收到最后一个数据包后才会在m_cat函数中拼接所有数据包并释放链表)。
1 | void |
任意地址写
任意地址写基于堆溢出,我们回顾一下刚才的ip_input函数,当IP_DF为0时调用ip_reass函数。当IP_MF不为1时(这里有个问题是为什么拿ipf_tos表示,正常对应ip包的service type位),即当前数据包为分包的最后一个,进入下面的循环进行链表数据包的拼接。
假设我们可以控制m->m_data以及m->m_len和n->m_data,就可以通过memcpy(m->m_data+m->m_len, n->m_data, n->m_len);拷贝可控数据到任意地址。
1 | static struct ip * |
exp中的arb_write逻辑如下。首先spray多次调用malloc清空堆内存,同主机建立connection从而申请得到so_rcv结构体,再发送一个MF为1的数据包,id为0xdead,触发分配0x668的mbuf,这个数据包刚好位于so_rcv的后面,我们通过write堆溢出覆写其m_data部分为指定地址(这里也可以部分写低地址)。之后再发送一个id相同,MF为0的数据包,触发合并,memcpy调用,send_ip_pkt(&pkt_info, write_data, write_data_len);将指定数据拷贝到m_data所在的地址。
地址泄露
泄露地址这个方法感觉非常巧妙,是拿icmp的响应包来实现的,既然都复习了IP协议,不妨多来看一眼tcp协议和icmp协议。如下图所示。
字段就不过多解释了,方便看exp的时候能对照上。
1 | * |

1 | struct icmp |
说回这里的leak方法。
- 首先通过堆溢出覆写m_data的低位为0xb00(因为该heap所在的内存页虚拟地址为0xxx000000),不会存在越界的问题。
- 通过任意地址写将伪造的icmp包写入到0x7fxxxb00+0x318+0x14+14处(eth报头14字节,IP报头0x14字节,m_len为0x318)
- 再来一次任意写,先connect得到so_rcv,再发送一个ICMP请求包,数据包的MF为1,其mbuf会被分配到so_rcv的后面
- 故技重施,利用so_rcv溢出到mbuf->m_data,改为0xb00+0x318+14+0x14(我们之前伪造的icmp包的位置)
- 发一个MF=0的包,触发ICMP的响应,得到伪造的icmp数据包及后面的脏数据,从而leak出text地址和heap地址。
劫持控制流
最后劫持控制流的方法还是用QemuTimer,在bss有个全局变量main_loop_tlg,类型为QEMUTimerList,其成员active_timers为QEMUTimer*类型的变量,我们在堆上伪造这两个变量,覆写bss的全局变量,伪造cb为system@plt,opaque为参数地址,当expire_time过完就会触发命令执行。
1 | .bss:00000000012C3900 main_loop_tlg QEMUTimerListGroup_0 <?> |
1 | // util/qemu-timer.c |
调试记录
raycp师傅的exp注释写的很详尽,不过中间有一些不太好理解的地方,这里记录了一下自己动态调试的过程备忘。
寻找地址的方法:payload里给特殊字符,gdb里find字符串定位关键数据结构。
- 第一次堆溢出覆写m_data为0xb00
- 通过任意地址写写入伪造的eth+ip+icmp包
- 第二次堆溢出覆写m_data为0xb00+0x14+0x318+14的icmp伪造包处
- 根据leak的数据反查内存
- 对比之后确认泄露的内存恰为我们输入的伪造icmp地址处,不过在输出前做了一次拷贝
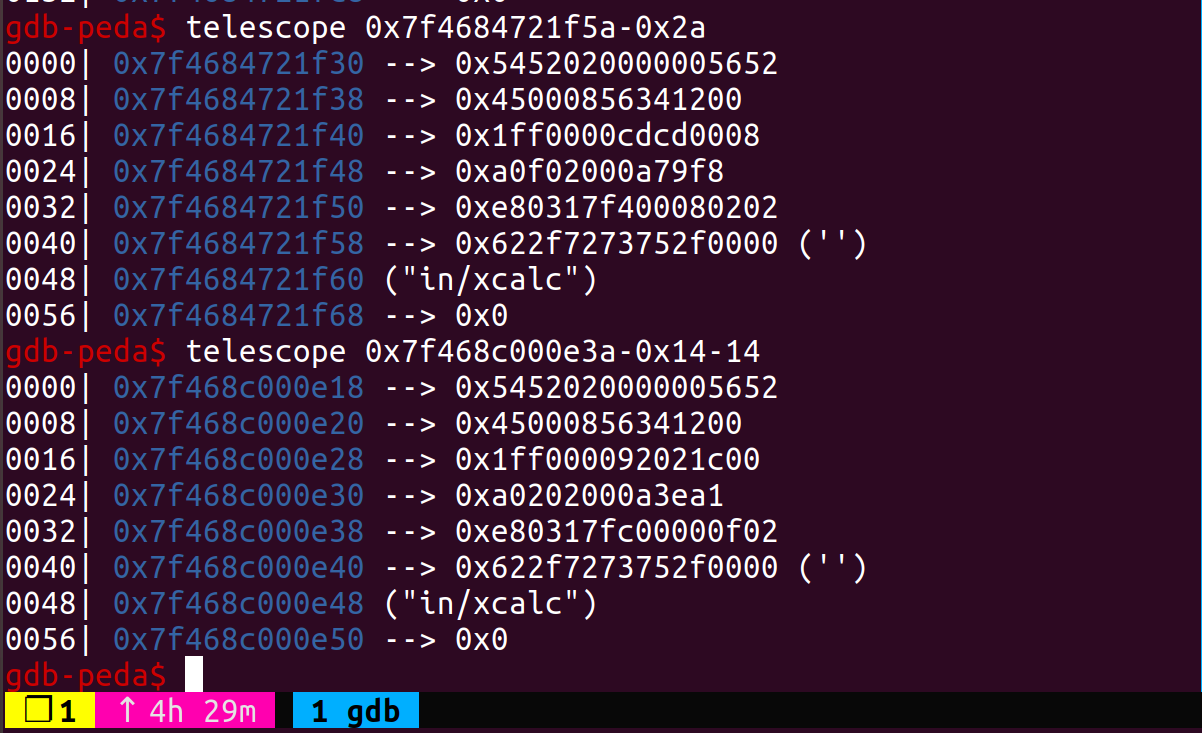
- 定位有效地址
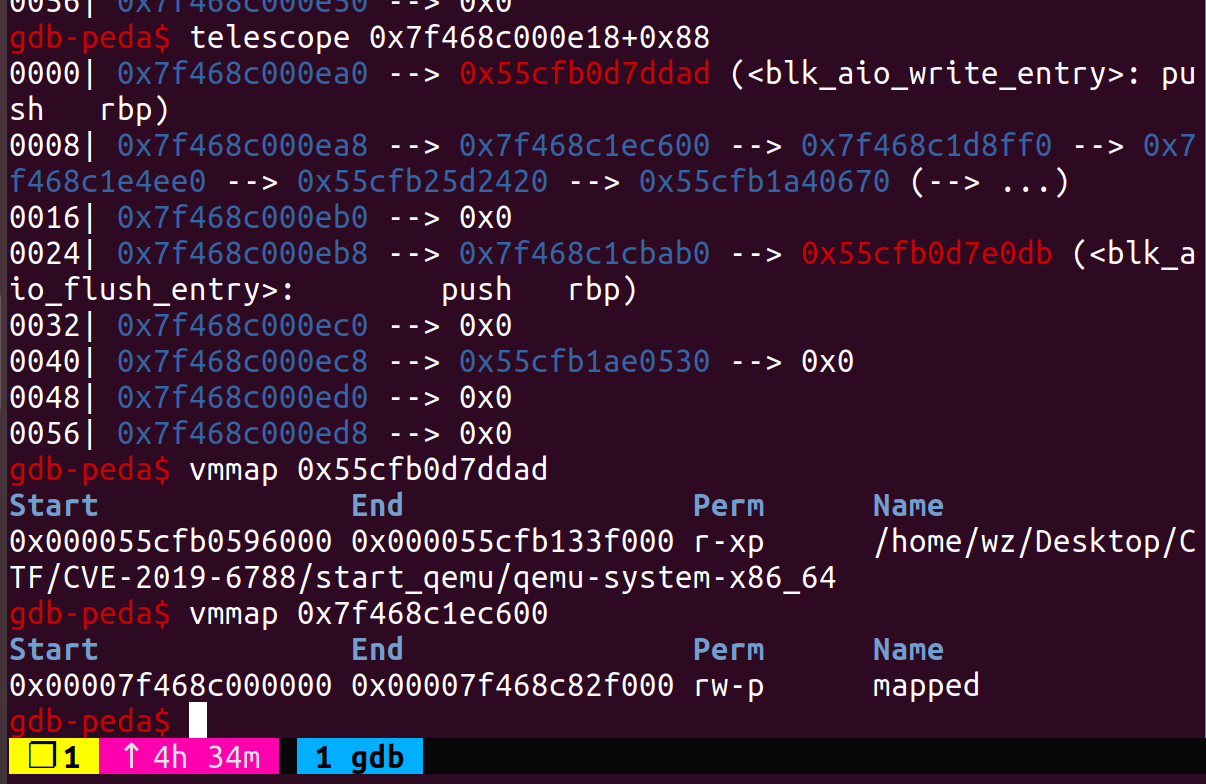
- 伪造timer_list和timer
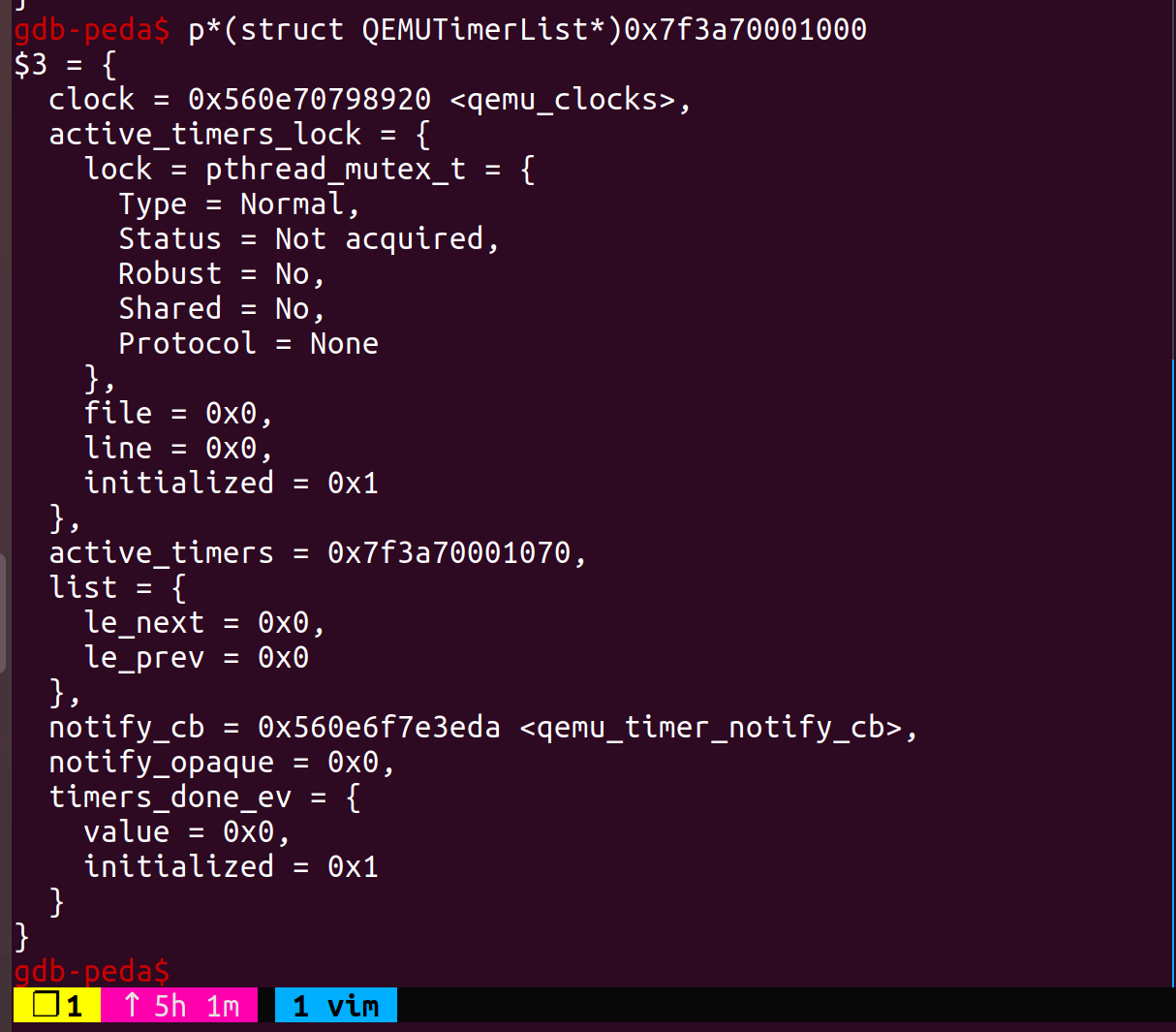
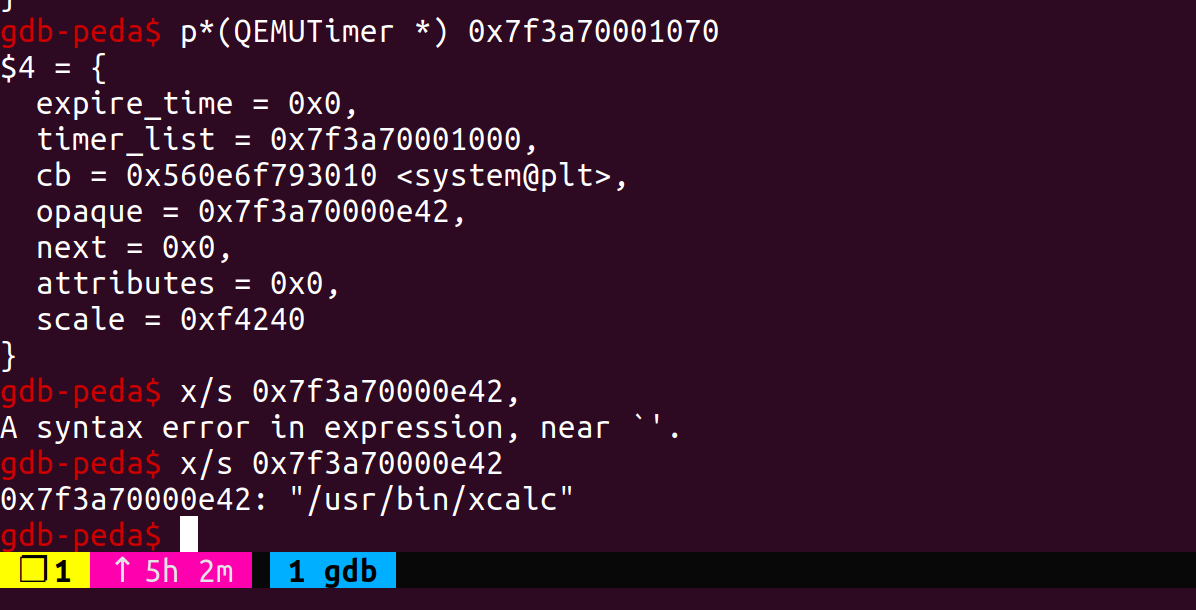
- 执行效果
exp.c
基本就是raycp师傅的代码,需要自己调试一下fake timer_list以及改system@plt地址。
1 |
|
漏洞patch
在memcpy前增加了长度检查。
1 | case EMU_IDENT: |
后记
搜这个CVE的时候看到了一个师傅的分析,其中引用的一个大佬的话发人深省。
最近在想分析漏洞究竟要到什么地步才算分析透彻,个人觉得能理解一个漏洞产生的原因,利用链以及挖掘相同漏洞的经验就算分析的比较透彻了,这也是我需要向raycp和其他师傅学习的东西。
最后的最后来点碎碎念,昨晚做梦跟一个尊敬的前辈聊天,问他我怎样才能进入xx实验室,前辈说我不够努力,是进不去的,醒来非常难受,希望寒假可以真真切切地做点事情。

